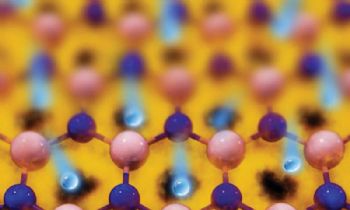
According to research from the University of Manchester, graphene could help to reduce the energy cost of producing heavy water and of decontamination in nuclear power plants, compared with current technologies.
The new development could lead to the reduction of CO
2 emissions associated with heavy-water production by up to a million tonnes a year.
Writing in
Nature Communications, a team from the University of Manchester led by Marcelo Lozada-Hidalgo demonstrated fully scalable prototypes of graphene membranes capable of producing heavy water. The research team says that producing heavy water — needed by the nuclear industry to generate ‘clean energy’ — is an expensive process.
“Because of graphene’s unique material properties, it has the potential to effectively separate sub-atomic particles, making this process more efficient and cost-effective. Separating hydrogen isotopes is a huge task for nuclear fission and future fusion plants.
“Thousands of tons of isotopic mixtures are processed every year. Yet, producing just 1kg of heavy water consumes enough energy to power an average American household for an entire year.”
Dr Lozada-Hidalgo said: “This is a crucial milestone in the path to taking this revolutionary technology to industrial application.
“The potential gains are high enough to justify its introduction in the highly conservative nuclear industry. We believe this technology can economically transform the environmental footprint of future nuclear plants.