 Open Mind Technologies
Open Mind Technologies has announced that US-based Ramco Machine, which is based in Massachusetts, used HyperMill CAM software and five-axis machining strategies to make parts for a NASA satellite mission.
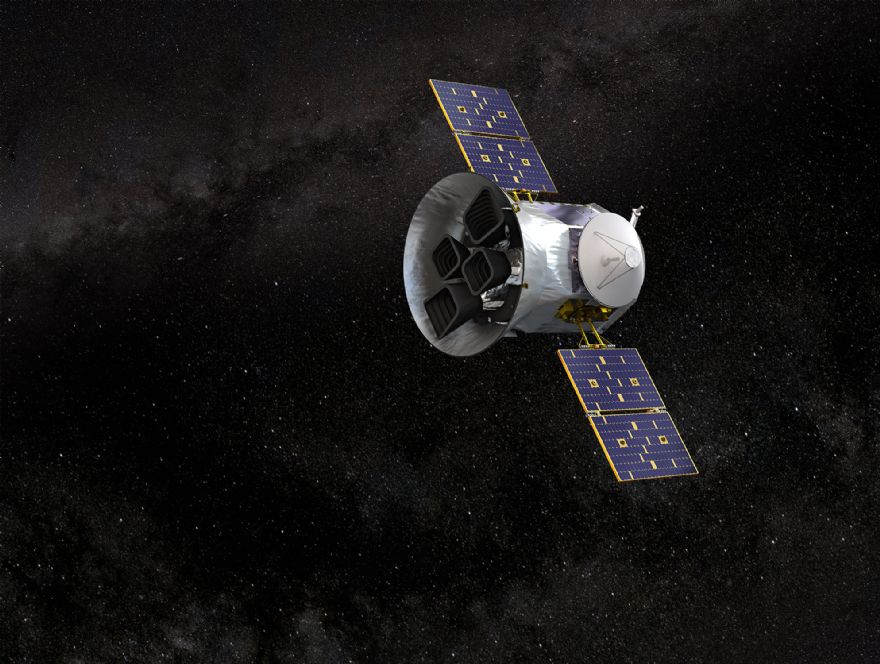
Named Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), this mission is credited with discovering the first circumbinary planet — a world orbiting two stars.
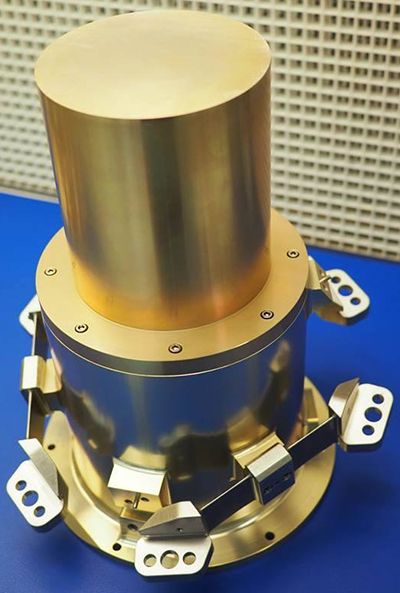
In 2017, Ramco was contracted by MIT Lincoln Laboratory (also in Massachusetts) to make the camera mount brackets for the TESS satellite mission, which is designed to explore and survey nearby bright stars to analyse planets, both smaller and larger than the Earth, as they circle their host stars and the Earth orbits the sun.
In 2018, a solar-powered in-space satellite equipped with four ultra-sensitive cameras was launched aboard a two-stage SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on its journey beyond Earth’s solar system to outer space.
The four-camera system developed at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory monitors the brightness of more than 200,000 stars and searches for minute drops in brightness as the planets transit in front of each star.
Making the mounting brackets required machining Invar, a nickel-iron alloy with a low thermal expansion coefficient, allowing it to meet the rigors of launch while enabling it to compensate for the extreme temperature swings of outer space.
The mounting bracket has tight tolerances, with the central rib having a thickness of 1.27mm ±0.025mm, the perpendicularity between surfaces held to 0.025mm and the bracket’s two opposing surfaces inline with each other to within 0.025mm.
To cut Invar and achieve the required tolerances, Ramco used five-axis ‘profile finish tool-paths’ generated by HyperMill to ensure accurate finishes and tolerances were achieved for each part.
Further details of the mission can be found at the Web site (
www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2020/nasa-s-tess-mission-uncovers-its-1st-world-with-two-stars).