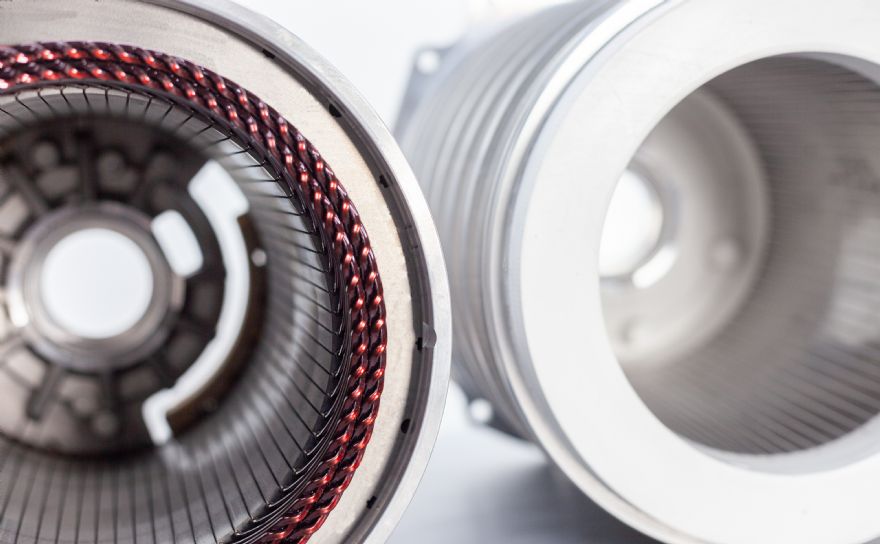
Heat is generated in an e-motor, sometimes quite a bit; and in demanding applications the motor electronics cause the power to be reduced or even shut the motor down completely. However, using a thermally conductive casting resin as a heat transfer medium can protect an electric motor from overheating without losing power — a principle sometimes referred to as a ‘static solid cooling system’.
Uwe Köhler began developing thermally conductive casting resins was already thinking about this in the 1990s and subsequently created Lambdapox, a product that offers a thermal conductivity of λ = 8W/mK. Sales and customer support for this product is being handled by Lambda Resins. Based in Kerpen (Germany), the company is a joint venture between the inventor of Lambdapox and the Nagel Group, from Nürtingen, Germany (the latter has has production lines for electric motor stators in its portfolio through its group company Gehring Technologies).
The Lambdapox resin is designed to thermally stabilise e-motors and enable continuous operations at high output levels. This is achieved by casting the stator winding of the motor with the resin in a vacuum process, thereby ensuring that the heat flows into the surrounding cooling jacket much faster than without this encapsulation, avoiding the problem of heat build-up in the winding. An alternative approach is forced cooling with oil, but systems based on this approach are complex and risk oil leaks.
Mr Köhler says Lambdapox easily withstands the heat shock test from -40 to over 180°C, and that the cracking often observed in potting materials in the past during these tests is not suffered by this resin. “Our casting resin causes a reduction in temperatures in the winding head of up to 40-60°C at the same load. Depending on the configuration, the motors achieve up to 50% higher continuous power at the same thermal load.; and while the cast resin is suitable for all high-performance motors, it is especially applicable to e-vehicles, where the focus can be either to maximise performance, or to minimise space requirements while keeping performance unchanged.
He concludes: “The field of e-mobility, in particular, benefits from the use of cast resin. Lower engine heating results in higher efficiency or lower energy requirements. In the end, the range of the vehicle is increased.”