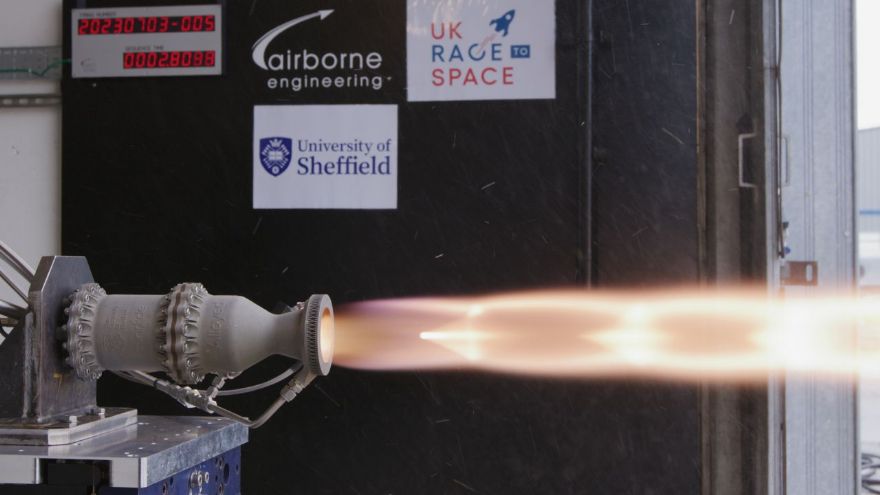
A liquid rocket engine - similar to the kind used by pioneering space companies such as SpaceX - has been 3-D printed by students at the
www.sheffield.ac.uk University of Sheffield. The ‘SunFire’ engine, developed by a team of Sheffield engineering and science students, is the first metallic 3-D printed liquid rocket engine to be built and successfully tested by students in the UK.
It is the most powerful student-built engine of its type - an engine that uses both fuel and an oxidiser rather than breathing in oxygen like a jet engine. It is also the first that is regen-cooled - an engine that uses fuel to cool the combustion chamber before it is burnt, which increases the engine’s efficiency and saves weight.
The Sheffield students have successfully ‘hot-fired’ the engine as part of a week-long competition called
Race to Space, in which teams of students from universities across the UK tested rocket engines in July they have built over the last two academic years.
The Race to Space competition week is believed to have set an unofficial world record itself, for the number of different hybrid/liquid rocket engines hot-fired for the first time on one site in one week.
There are only a handful of liquid rocket engines made by students throughout Europe and even fewer regen engines worldwide, and until now, none in the UK as powerful as the 3-D printed engine built in Sheffield.
The Sheffield students built the engine outside of their studies as part of the University of Sheffield’s Space Initiative - a programme to help STEM students use their skills to tackle some of the space industry’s biggest challenges and help them develop careers in the industry after graduation.
Students in the team - known as Sunride - hope to eventually use the engine to power one of their own rockets to the edge of space and become the first UK student-led team to launch beyond the Kármán line which borders Earth's atmosphere 62 miles above sea level. The team already holds the UK altitude record for an amateur rocket, which they achieved in 2019.
The University of Sheffield’s Royce Discovery Centre - a research centre developing the next generation of materials to meet the needs of UK manufacturing - was instrumental in trialling the laser-powder-bed metallic 3-D printing system that was used to build the engine. The University’s Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC) and Faculty of Engineering were also involved.
Henry Saunders - who led the team last year and is now doing a PhD at the University of Sheffield’s Royce Discovery Centre in 3-D printing, said: “The hot-fire test of our engine was a day I will never forget. From coming up with the idea in a coffee shop with two friends over two years ago, it was amazing when we finally got to fire our very own rocket engine.
“Being involved with the SunFire programme provided me with an opportunity to take the engineering science I had learned about in lectures and translate these learnings into a real-world practical application. This for me was where the real excitement and learning reinforcements came from, not just seeing a rocket engine on a PowerPoint slide with some equations next to it, but actually being involved in building a rocket engine from scratch. The equations only get you so far, the real learning, for me, came from trying things, failing and then eventually succeeding.”
Engineering graduate and former Sunride project manager, Dana Arabiyat - who is now working at Rolls-Royce, said: “Two years and countless hours of hard work later, the successful hot-fire of our engine got us jumping for the most unforgettable five seconds of our lives! This achievement is a testament to the incredible talent and commitment of our Project SunFire team members and leads, and to the tireless mentorship and supervision of Dr Alistair John.”
Dr Alistair John, deputy director of aerospace engineering at the University of Sheffield, who supervised the team, said: “3-D printing is increasingly being used by rocket companies such as SpaceX as it allows the build of complex, lightweight custom geometries that would not be possible using traditional methods. For example, the cooling channels in our engine, which stop the engine melting despite the 2,000°C combustion temperature, can only be constructed using 3-D printing.
“Extra-curricular activities such as
Sunride and the
Race to Space initiative are hugely important as they allow students to apply the knowledge from their degree and push the boundaries of what they can achieve. It is hugely important for the UK space sector that we give our students hands-on, practical experience to develop the skills industry needs.”